Creating a Widget
Introduction
What are Widgets
Simply put, widgets are configurable components that make up a Dashboard. Widgets come in a variety of types; each type
is designed to show a different type of content to user, and, provided that the dashboard has a configured update
interval, keep the display up-to-date if the content changes. A widget is a configurable JavaScript module that is
rendered on the dashboard grid as a Backbone View. Widgets can be configured using the dashboards.json
configuration file and can take a custom settings object.
Note: For more information on the configuration file, please see the Find Admin Guide.
Assumptions and Constraints
- A widget’s layout must be flexible. The grid system we have implemented allows a widget to be configured to occupy a rectangle of any size or proportion. A widget’s layout must accommodate reasonable configurations without breaking the UI.
- A widget’s layout must be responsive, and adapt its layout when the browser window is resized or maximised.
- The widget should not take a long time to load and update. Dashboard systems are expected to show up-to-date information, therefore loading in a timely manner is essential.
- The widgets should all run as separate instances and not interfere with other widgets.
- A widget is non-interactive. Widgets should only display information, and their readability must not depend on the user being able to mouseover or scroll them.
- If a dashboard has a configured update interval, all of its updateable widgets will be periodically refreshed, i.e. fetch fresh data and update their displays accordingly. Such widgets must detect changes to their data and have ways to re-render their display without requiring the user to reload the page in the browser.
Widget Examples
Topic Map Widget
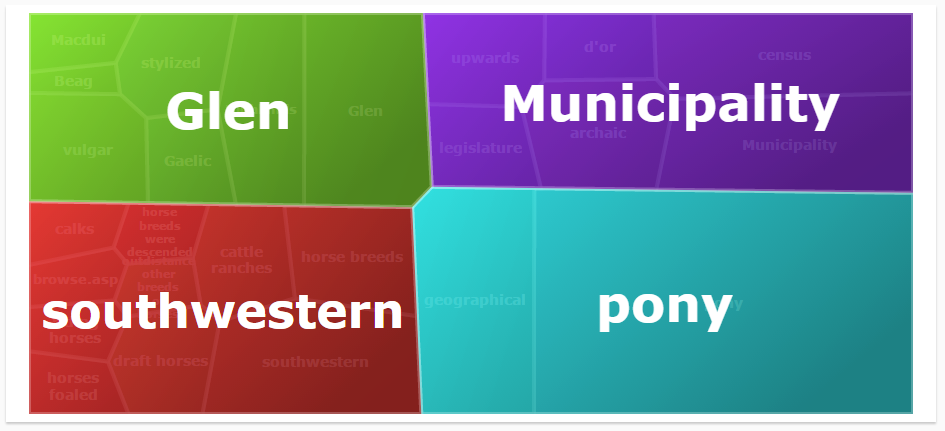
The Topic Map Widget is one of the standard built-in widgets which is backed by a saved search (explained here).
Current Time and Date Widget
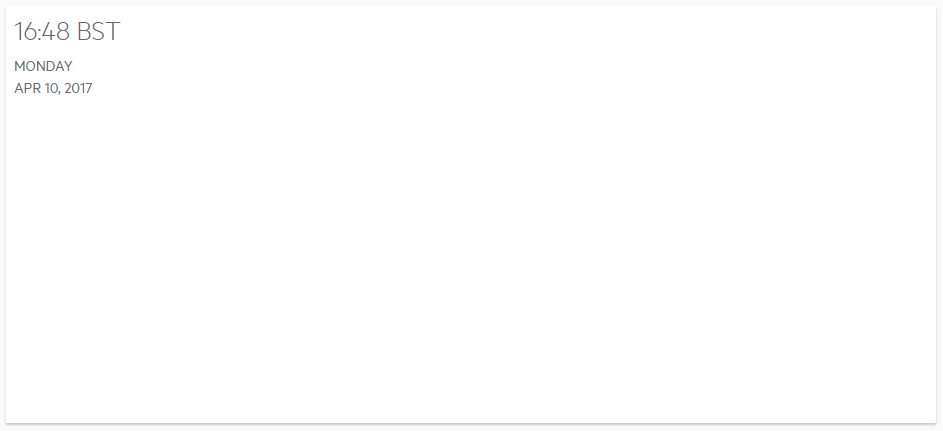
The Current Time and Date Widget is an example of a Standard Widget (explained here). This is not backed by any data from the server and will not update periodically.
Results List Widget

Like the Topic Map Widget, the Results List Widget is backed by a saved search and will display the
top n results as specified in the configuration file. The Results List Widget will alter its layout so that the
results best fit its configured shape and size. If the configured widget size is too small to display all the
requested results, excess entries will be hidden.
Widget Types
HPE Find currently supports three types of widgets.
These three widget types should cover most use cases and can all be implemented quickly by extending their abstract
views (widget.js, updating-widget.js, and saved-search-widget.js, respectively) which can be found in the
widgets folder:
webapp/idol/src/main/public/static/js/find/idol/app/page/dashboard/widgets/
Standard Widget
A Standard Widget is designed to be largely static. The widget itself can change (see the Current Time and Date Widget), but it must not depend on the dashboard’s update infrastructure to do so. It will be rendered once, and is in sole control of any changes that happen to it thereafter. For example: a widget to display a promotional HTML page.
Note: If the widget is just a static piece of HTML or an image, then the built-in Static Content Widget or Static Image Widget should be used, respectively. Refer to the Admin Guide for configuration details.
Updating Widget
An Updating Widget is the same as a Standard Widget, but will be updated by its dashboard every
n seconds as defined in the updateInterval property set in the dashboards.json configuration file. On update, the
dashboard calls the widget’s doUpdate() function which must be implemented to fetch new data (if necessary) and update
the display. This type of widget should be used when there is a need to periodically fetch data or re-render. For
example a widget to display the weather may poll the API of a third-party weather service.
Note: If your widget depends on data held in a Saved Query or Saved Snapshot, use the Saved Search Widget instead.
Saved Search Widget
The Saved Search Widget is an extension of the Updating Widget that is backed by a saved search. It
implements its own flavour of the doUpdate() function and will re-fetch the saved search data, which can then be
used to retrieve any additional information needed by the widget to update its display. For example, the
Results List Widget relies on fetching the Document Collection, and the
Topic Map Widget requires Related Concepts fetched by the Entity Collection.
Note: A Saved Search can be either a Query or a Snapshot. As Snapshots do not change after creation, a widget backed by a Snapshot will never update.
Development
Shared Development
Widget Registry
All widgets are located and instantiated via the widget registry (widget-registry.js). This is where the widget
source files are loaded via Require.js. When a widget is loaded by the dashboard, it uses the name
specified in the configuration file to perform a lookup in the widget registry to retrieve the constructor.
A widget registry entry looks like this:
SunburstWidget: {
Constructor: SunburstWidget
}
The key for the object property (SunburstWidget) is the widget type property of the new widget in the
dashboards.json configuration file. The Constructor property should be the Backbone.js View constructor for the
widget view. Widgets should be written in a separate file and loaded via Require.js into the registry.
HTML and Layout
The layout of the widgets is very simple: each widget has a title (hidden by default) and a content div. Both use
display: flex, so if the title bar is hidden, the content will expand to take up 100% of the widget’s height. For
the purposes of widget development, the only element of consequence is the widget content div. This is passed to the
view from the abstract widget as this.$content and is available after calling the render method on the widget
abstract view. For example:
// (AbstractView) can be Widget, UpdatingWidget, or SavedSearchWidget. It must be imported via Require.js.
(AbstractView).prototype.render.apply(this); // this.$content is defined here
this.$content.html(someHtml);
As explained in the Admin Guide, the widgets are sized and laid out in a grid pattern. The size of the grid is specified on a per-dashboard basis. This is handled by the infrastructure of the dashboard page. Because of this, the widget must be capable of handling multiple alternate layouts: for example the Results List Widget may be configured to have row- or column-based layout, according to the proportions of its bounding rectangle.
Functions and Properties
All widget types have the property clickable. It takes a Boolean value and determines whether the widget
click handler is called when the user clicks the widget. As mentioned above, the widget should be primarily
non-interactive and must not depend on user click actions to be usable.
The onResize function handles window resize events which should be overridden with logic that resizes or redraws the
widget. This funciton will be called automatically when the window is resized, and also when the sidebar is toggled.
The onClick method may be used to handle click functionality and will be called if the widget is clicked anywhere.
This will only be called if the clickable property is set to true.
Note: A Saved Search Widget already defines its own a click handler, which navigates the user to the underlying Saved Search. Unless this behaviour is undesirable, do not override the
onClickmethod when implementing a Saved Search Widget.
The onHide method may be used to implement any commands a widget must execute when the user hides (e.g. leaves)
the dashboard. For example, the built-in Video Widget uses this function to stop the playback, so that the video does
not play in the background once the user had navigated away. There is no need to call onHide() yourself - it will be
called automatically by the dashboard page when necessary.
Widget Settings
In the configuration file each widget can have a widgetSettings.
{
// ... Other options like widget name, type, size and position go here
"widgetSettings": {
"key": "some value",
"key2": {
"subkey": "another value",
"subkey2" : [1,2,3,4,5,6]
}
}
}
These values are passed in to the widget when it is initialised, and stored as a variable on the view. For example the above would be accessed via:
initialize: function(options) {
Widget.prototype.initialize.apply(this, arguments);
this.key = this.widgetSettings.key;
this.key2 = this.widgetSettings.key2;
this.subkey = this.widgetSettings.key2.subkey;
this.subkey2 = this.widgetSettings.key2.subkey2;
}
Standard Widget Development
The standard widgets are very simple and utilise nothing additional to the above shared settings when implemented.
Most uses of this type of widget could be replaced with a StaticContentWidget or StaticImageWidget.
Example
define([
'./widget' // load the abstract widget view.
], function(Widget) {
'use strict';
return Widget.extend({
initialize: function(options) {
Widget.prototype.initialize.apply(this, arguments);
// configuration determines whom to greet.
this.subject = this.widgetSettings.subject || 'world';
},
// onClick: function(){
// // optionally implement click handler here
// },
// onResize: function(){
// // optionally implement resize handler here
// },
render: function() {
Widget.prototype.render.apply(this);
// render HTML greeting
this.$content.html('<h1>Hello, ' + this.subject + '!</h1>');
}
});
});
Updating Widget Development
The updating widget utilises a set of functions to handle the update. These functions need to be implemented carefully
to ensure that the widget works with the TimeLastRefreshedWidget (this is a widget which tracks the dashboard update
cycle and displays this information to the user).
Functions
doUpdate(done) is the main update function that is called when the dashboard refreshes all of the widgets. The done
parameter is a callback that must be called when the widget has finished updating; if it is not called the
TimeLastRefreshed widget will not know that the update has finished and the loading spinner will not be hidden. This
function should re-fetch any data needed to render the widget and then update the UI accordingly. The loading spinner
is handled by the abstract view and, apart through calling done() at the end of an update, does not need to be
shown and hidden manually.
onCancelled is called when the update had been cancelled for any reason. This function should cancel any pending
requests made by the widget and resolve or remove any outstanding promises.
Example
define([
'./updating-widget', // load the abstract updating-widget view.
'./path/to/some-weather-service' // load some weather service.
], function(UpdatingWidget, SomeWeatherService) {
'use strict';
return UpdatingWidget.extend({
initialize: function(options) {
UpdatingWidget.prototype.initialize.apply(this, arguments);
// configuration determines whom to greet.
this.subject = this.widgetSettings.subject || 'world';
// create some weather service with a location from the settings.
this.weatherService = new SomeWeatherService({location: this.widgetSettings.location});
},
render: function() {
Widget.prototype.render.apply(this);
// render some html greeting with a weather option.
this.$content.html('Hello, ' + this.subject + '! The weather near you is: <span class="weather-description"></span>');
},
doUpdate(done) {
this.weatherService.getWeather({ // perform some fetch on the weather service.
success: function(weather) {
// display the weather inside the dedicated <span> element
this.$('.weather-description').html(weather);
done(); // call this to show that the update is complete
},
error: function() {
// Clear away the out-of-date weather
this.$('.weather-description').empty();
// Display error message
this.$('.weather-description').text('An error has occurred.');
done(); // call this to show that the update is complete
}
})
},
onCancelled: function() {
if(this.weatherService.requestInProgress()) { // if the weather service is fetching.
this.weatherService.cancelRequest(); // perform some request cancellation.
}
}
});
});
Saved Search Widget Development
Saved Search Widgets are an extension of the Updating Widget they have their own version of the
doUpdate and onCancelled methods, which must not be overridden unless the prototype function is called as well.
The abstract view handles the retrieval of the saved search during initialisation and updates, and displays an error
message if any stage of the update fails.
Functions
postInitialize (optional) is a function that is run after the saved search has been fetched successfully on initialisation.
This can optionally return a promise in which case getData will not be called until it has been resolved. This is
useful for loading any extra objects or views that are contingent on the information in the saved search. Barring
connection errors, this function will only be called once during the life of the widget, therefore it should not be
used to fetch information that need to be refreshed periodically.
getData is the main method for retrieving the data needed to render the view. It must return a promise, which will
be used to handle the doUpdate callback. This function will be called on every update cycle. For example, in the
Results List Widget this function is used to fetch the Document Collection. The widget creates a
listener on the collection which renders the new results and calculates what can be displayed.
isEmpty (optional) should contain logic that determines if the saved search returned no data. This information is used to
display a generic “The query returned no results” message, which is distinct from an error message. Have this function
return true if an update returned no data, or false otherwise. Default implementation always returns false.
updateVisualizer (optional) to avoid issues with sizing SVG-based visualizers, this method should call any code
responsible for (re)drawing the visualizer.
Properties
savedSearchModel is the model that controls the saved search information. This is controlled by the abstract view
and should be considered read-only.
queryModel is available if required. This contains the same information as the saved search model in a
different format and is mainly used for internal purposes.
viewType is the results view (List, Topic Map, Sunburst, etc.) that clicking the widget will navigate to. This
property is optional.
Example
define([
'underscore', // import underscore for templating.
'./saved-search-widget', // import the abstract saved search widget.
'find/app/model/documents-collection', // import the documents collection.
'moment' // import moment for parsing dates and timestamps
], function(_, SavedSearchWidget, DocumentsCollection, moment) {
'use strict';
return SavedSearchWidget.extend({
// When the widget is clicked take user to the saved search with the list view displayed.
viewType: 'list',
// template for the document.
template: _.template('<span>Latest result is: <%-title%> <br> it was indexed on: <%- date %></span>'),
initialize: function(options) {
SavedSearchWidget.prototype.initialize.apply(this, arguments);
this.documentsCollection = new DocumentsCollection(); // create the collection.
// add a Backbone.js listener to alter the html when a new model is added
this.listenTo(this.documentsCollection, 'add', function(attributes) {
this.$content.html(this.template({
title: attributes.title,
date: moment(attributes.date).format()
}))
});
},
getData: function() {
// Fetch the document collection based on the saved search; return the resulting promise.
return this.documentsCollection.fetch({
data: {
text: this.queryModel.get('queryText'),
max_results: 1,
indexes: this.queryModel.get('indexes'),
field_text: this.queryModel.get('fieldText'),
min_date: this.queryModel.getIsoDate('minDate'),
max_date: this.queryModel.getIsoDate('maxDate'),
sort: 'date',
summary: 'context',
queryType: 'MODIFIED',
highlight: false
},
reset: false
});
}
});
});